Battery-related concerns are one of the major hurdles to the wide adoption of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV). A newly published paper by Warren B. Nelms Institute researchers aims to address these concerns with SAVIOR, an innovative Internet-of-Things (IoT) framework for replenishing BEV batteries on-the-go with the help of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and mobile charging stations (MoCS).
The paper titled, “SAVIOR: A Sustainable Network of Vehicles with Near-Perpetual Mobility” was published in IEEE Internet of Things Magazine in June 2023. This paper is authored by
Abstract:
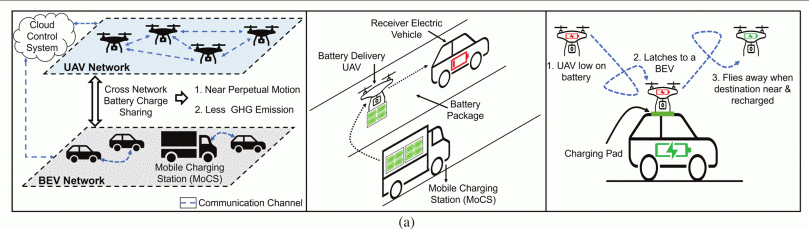
Switching to Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV) can have a significant positive impact on our environment. However, the adoption of BEVs is vastly impeded by battery-related concerns, such as limited travel range, long charging time, high purchasing cost (battery-induced) and lack of charging stations. Additionally, it is very expensive to build a large infrastructure of fast charging stations that can cater to a full-scale BEV fleet. Alternative solutions, such as charging from the road and BEV-to-BEV stationary charge sharing, have been proposed to counteract range anxiety, but they are mostly ineffective and suffer from scalability issues. In this article, we present SAVIOR, an innovative Internet-of-Things (IoT) framework for replenishing BEV batteries on-the-go with the help of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and mobile charging stations (MoCS). This will allow rapid BEV battery replenishment, eliminating the need for BEVs to make prolonged and pre-planned halts for re-charging. We also observe that package delivery UAVs can utilize this framework to make long-distance trips with the help of mobile charging stations and BEVs. We quantitatively analyze the effectiveness of such a framework through a simulation platform that we have developed. There is a drastic improvement in the mobility of BEVs and UAVs. Through statistical analysis, we also observe that greenhouse gas emissions (even for BEVs and UAVs) can be significantly reduced by SAVIOR if the MoCS are powered by renewable energy sources (e.g., solar).
Read the full paper on IEEE Internet of Things Magazine, Volume 6: Issue: 2.